Dynamic Programming¶
难点¶
- 如何在分析最后一步时选择正确角度并考虑所有可能情况,进而写出状态转化方程. i.e. Buy and Shell stock, Edit distance, Longest Increasing Subsequence.
Knapsack problems¶
The knapsack problems often given the follow conditions
N, the number of itemsM, the size of the knapsacks[i], the size of the itemi.v[i], the value of the itemi.c[i], the maximum time itemican be used.c[i]could be an all1array, hence 0-1 knapsack problem.c[i]could also beinf, meaning the items can be used as many time as you want (bounded by the size of the knapsack).
Knapsack problems ask
- Whether the given items can fit into the size of the knapsack.
- Find the maximum capacity the items can occupy the knapsack.
- Find the maximum value of items that can fit into the knapsack.
- Find the total number of ways the given item can fit into the size of the knapsack. (reuse is allowed)
In all the above questions, the items can be reused or not reused, they are very different and the throught process and the solution are also different.
Knapsack I¶
- Given
N,M,s[i], find the maximum size you can put into the Knapsack.
class Solution {
public:
int backPackI(int m, vector<int> A) {
int n = A.size();
if (n == 0) return 0;
bool f[n + 1][m + 1];
f[0][0] = true;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {
f[0][j] = false;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j <= m; ++j) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
if (j >= A[i - 1]) {
f[i][j] = f[i][j] || f[i - 1][j - A[i - 1]];
}
}
}
for (int j = m; j >= 0; --j) {
if (f[n][j] == true)
return j;
}
return 0;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int backPackI(int m, vector<int> A) {
int n = A.size();
if (n == 0) return 0;
bool f[m + 1];
f[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = m; j >= 0; --j) {
f[j] = f[j - 1]
if (j >= A[i - 1]) {
f[j] = f[j] || f[j - A[i - 1]];
}
}
}
for (int j = m; j >= 0; --j) {
if (f[j] == true)
return j;
}
return 0;
}
}
Knapsack II¶
-
Given
N,M,s[i],v[i], find the maximum value you can put into the Knapsack. -
思考方式任然是从最后一个物品选还是不选,只是我们现在考虑的是价值。此时状态就不能是可行性(Backpack)或者多少种了(Backpack V), 我们要纪录总价值。
- state
f[i][w]: 表示前i个物品能拼成重量w的总价值(V)。 - state transition equaltion:
f[i][w] = max(f[i−1][w], f[i−1][w−A[i−1]]+V[i−1]|w≥A[i−1]且 f[i−1][w−A[i−1]]≠−1) - Initialization: f[0][0] = 0, f[0][1] = -1, ... f[0][w] = -1. -1 代表不能被拼出。
class Solution {
public:
/**
* f[i][w]: 前i个物品能够拼成w的总价值
* f[i][w] = max(f[i - 1][w], f[i - 1][w - A[i - 1]] + V[i - 1])
*/
int backPackII(int m, vector<int> A, vector<int> V) {
int n = A.size();
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int f[n + 1][m + 1];
/* init */
f[0][0] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
f[0][j] = -1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j]; /* 此处必须初始化 */
if (f[i - 1][j - A[i - 1]] != -1 && j >= A[i - 1]) {
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - A[i - 1]] + V[i - 1]);
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
if (f[n][j] != -1 && f[n][j] > res) {
res = f[n][j];
}
}
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
/**
* f[i][w]: 前i个物品能够拼成w的总价值
* f[i][w] = max(f[i - 1][w], f[i - 1][w - A[i - 1]] + V[i - 1])
*/
int backPackII(int m, vector<int> A, vector<int> V) {
// write your code here
int n = A.size();
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int f[m + 1];
/* init */
f[0] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
f[j] = -1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = m; j >= 0; j--) {
if (f[j - A[i - 1]] != -1 && j >= A[i - 1]) {
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - A[i - 1]] + V[i - 1]);
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
if (f[j] != -1 && f[j] > res) {
res = f[j];
}
}
return res;
}
};
Knapsack III¶
- Given
N,M,s[i],v[i], find the maximum value you can put into the Knapsack while reuse is allowed - Even though you can reuse, it is not limited, you can use items
iat mostm / s[i]times. In this sense, this problem is equivalent to the problem Knapsack IV. -
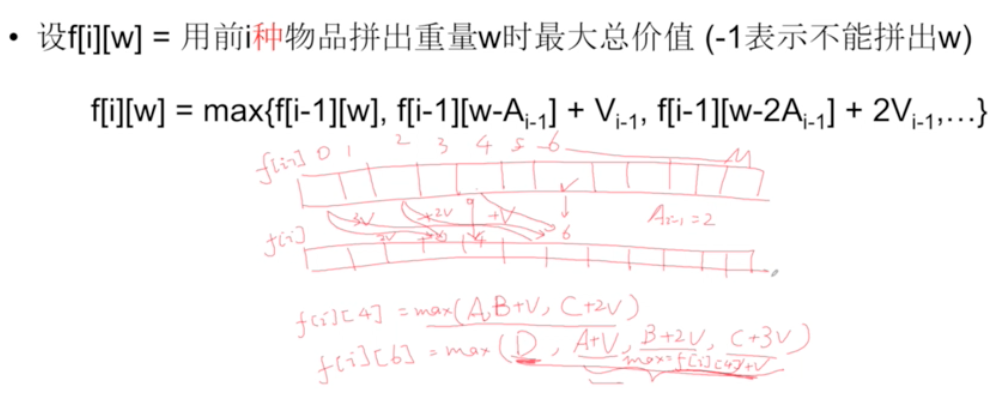
From O(MNK) to O(MN): notice the third loop can be optimized by closely looking for the redundant computation. For each
iandj, we check allks for the value off[i - 1][j - k * A[i - 1]]to updatef[i][j]. We can remove some of the redundant computation. Because the innermost loop will always look back an integer multiple ofs[i]of the previous rowf[i - 1]. For eachi, we only looking for multiple times ofs[i - 1]index before. We can use previous results directly for the current calculation then addv[i]instead of restart fromk = 0. This way we can get rid of the inner most loop. See the below diagram and sketch for the derivation of the state equation change. As a result, the solution code is very similar to the problem Knapsack II, except the single difference in indexing (iinstead ofi - 1). but they are completely different, the similarity of the code is pure a coincidence.j 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 f[i-1] x x x x x x x x x x s[i] v v v 2 f[i][4] = max(f[i - 1][j - 0*2], f[i - 1][j - 1*2] + 1*v[i - 1], ...) f[i][6] = max(f[i - 1][j - 0*2], f[i][4] + v[i - 1]) = max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - s[i - 1]] + v[i - 1])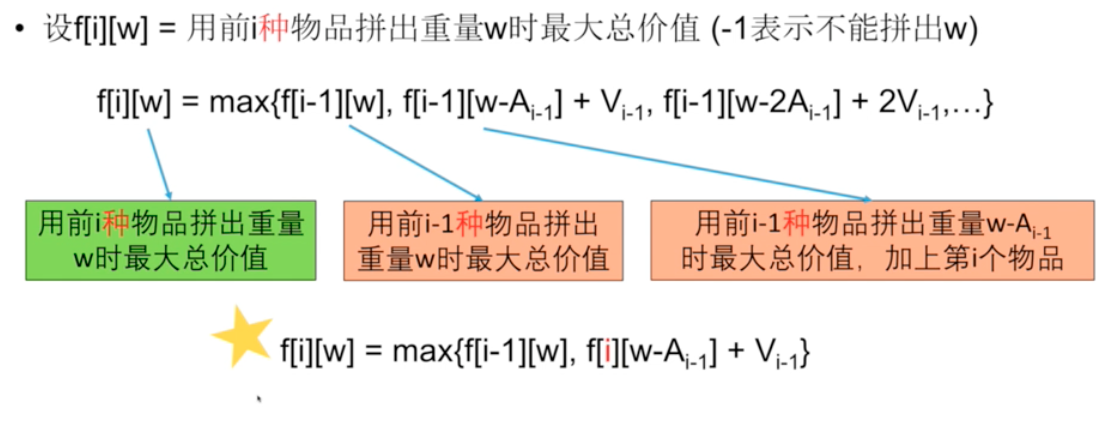
-
From O(MN) to O(M): This is from the following observation explained using the figure. It is a very clever idea in noticing that the new value only calculated from the the front index
j - k*s[i-1]and the the old value from the same index (hence thejis iterating from0in the O(M) solution, in contrast, the O(M) solution in Knapsack II iteratejbackward because need the old value not the new ones).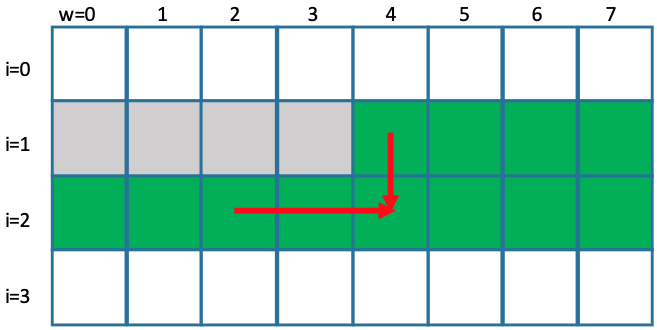
class Solution {
public:
int backPackIII(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& V, int m) {
int n = A.size();
int f[n + 1][m + 1];
f[0][0] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < m; ++j) {
f[0][j] = -1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
for (int k = 0; k <= m / A[i - 1]; ++k) {
if (f[i][j - k * A[i - 1]] != -1 && j >= k * A[i - 1]) {
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - k * A[i - 1]] + k * V[i - 1]);
}
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int j = 0; j <= m; ++j) {
if (f[n][j] != -1 && f[n][j] > res)
res = f[n][j];
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int backPackIII(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& V, int m) {
int n = A.size();
int f[n + 1][m + 1];
f[0][0] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < m; ++j) {
f[0][j] = -1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
if (f[i][j - A[i - 1]] != -1 && j >= A[i - 1]) {
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i][j - A[i - 1]] + V[i - 1]);
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int j = 0; j <= m; ++j) {
if (f[n][j] != -1 && f[n][j] > res)
res = f[n][j];
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int backPackIII(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& V, int m) {
int n = A.size();
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int f[m + 1];
/* init */
f[0] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
f[j] = -1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
if (f[j - A[i - 1]] != -1 && j >= A[i - 1]) {
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - A[i - 1]] + V[i - 1]);
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
if (f[j] != -1 && f[j] > res) {
res = f[j];
}
}
return res;
}
};
Knapsack IV¶
- Given
N,M,s[i],v[i],c[i], find the maximum value you can put into the Knapsack while the max time of usage of each item is given inc[i].
Knapsack V¶
- Given
N,M,s[i], find the number of possible Knapsack fills if each item can be used once.
class Solution {
public:
int backPackV(vector<int>& nums, int T) {
int n = nums.size();
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int f[n + 1][T + 1];
f[0][0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= T; j++) {
f[0][j] = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= T; j++) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
if (j >= nums[i - 1]) {
f[i][j] += f[i - 1][j - nums[i - 1]];
}
}
}
return f[n][T];
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int backPackV(vector<int>& nums, int T) {
int n = nums.size();
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int f[T + 1];
f[0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= T; j++) {
f[j] = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = T; j >= 0; j--) {
//f[j] = f[j - A[i - 1]] ==> f'[j]
if (j >= nums[i - 1]) {
// f'[j]
// cover old f[j]
f[j] += f[j - nums[i - 1]];
}
}
}
return f[T];
}
};
Knapsack VI¶
- Given
N,M,s[i], find the number of possible Knapsack fills if each item can be used unlimited times. - 这道题等同于Leetcode里 Combinations Sum IV
- 这里可以随便取,似乎题目变得无法下手,考虑“最后一步”这个技巧不能用了,因为最后一步可以是任意一个了。
- 但仍然可以用子问题来考虑。先不管最后一步是哪一个,最后一步之前的相加的总和一定是 Target - x. 这样就转化成一个子问题可以用DP来做。
- 具体做法我们可以对于每一个小于“总承重”的重量进行枚举最后一步x。可能的x是 A[0], ..., A[i - 1] 中任意一个.
Compare With knapsack V, how to deal with the unlimited usage
class Solution {
public:
int backPackVI(vector<int>& nums, int T) {
int n = nums.size();
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int f[T + 1];
f[0] = 1;
/* for each sub problem */
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {
f[i] = 0;
/* enumerate the last step */
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i >= nums[j]) {
f[i] += f[i - nums[j]];
}
}
}
return f[T];
}
};
// Suppose we also interested in print one of the possible solution. How could we change the code?
// f[i]: 存多少种方式
// pi[i]: 如果 f[i] >= 1, 最后一个数字可以是pi[i]
class Solution {
public:
int backPackVI(vector<int>& nums, int T) {
int n = nums.size();
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int f[T + 1];
/* pi[i]: 如果i可拼出(f[i] >= 1), 最后一个是pi[i] */
int pi[T + 1];
f[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {
f[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i >= nums[j]) {
f[i] += f[i - nums[j]];
/* 最后一个是nums[j]的可拼出i */
if (f[i - nums[j]] > 0) {
/* 纪录下来 */
pi[i] = nums[j];
}
}
}
}
if (f[T] > 0) {
int i = T;
cout << i << "=" << endl;
while (i != 0) {
// sum is i now;
// last number is pi[i]
// previuos sum is i - pi[i]
cout << pi[i] << endl;
i -= pi[i];
}
}
return f[T];
}
};
Race Car¶
waymo
坐标型¶
Triangle¶
Unique Paths¶
Unique Paths II¶
Minimum Path Sum¶
Bomb Enemy¶
Dungeon Game¶
221. Maximal Square¶
- Solution 1 monotonic stack
- Solution 2 Dynamic Programming
class Solution {
public:
int maximalSquare(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {
if (matrix.empty()) return 0;
int m = matrix.size();
int n = matrix[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> sum(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
sum[i][j] = matrix[i - 1][j - 1] - '0'
+ sum[i - 1][j]
+ sum[i][j - 1]
- sum[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
int area = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
for (int k = min(m - i + 1, n - j + 1); k > 0; --k) {
area = sum[i + k - 1][j + k - 1]
- sum[i + k - 1][j - 1]
- sum[i - 1][j + k - 1]
+ sum[i - 1][j - 1];
if (area == k * k) {
res = max(res, area);
break;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int maximalSquare(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {
if (matrix.empty()) return 0;
int m = matrix.size();
int n = matrix[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> sizes(m, vector<int>(n, 0));
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
sizes[i][j] = matrix[i][j] - '0';
if (sizes[i][j] == 0) continue;
if (i > 0 && j > 0)
sizes[i][j] = min(min(sizes[i - 1][j - 1], sizes[i - 1][j]), sizes[i][j - 1]) + 1;
res = max(res, sizes[i][j] * sizes[i][j]);
}
}
return res;
}
};
class Solution:
def maximalSquare(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:
res = 0
m = len(matrix)
n = len(matrix[0])
dp = [[0 if matrix[i][j] == "0" else 1 for j in range(n)] for i in range(m)]
for i in range(1, m):
for j in range(1, n):
if dp[i][j] > 0:
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1
res = max([max(row) for row in dp])
return res ** 2
1277. Count Square Submatrices with All Ones¶
- solution 1 Similar to 221. Maximal Square
class Solution:
def countSquares(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> int:
res = 0
for i in range(0, len(matrix)):
for j in range(0, len(matrix[0])):
if matrix[i][j] > 0 and i > 0 and j > 0:
matrix[i][j] = min(matrix[i - 1][j], matrix[i][j - 1], matrix[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1
res += matrix[i][j]
return res
序列型¶
Perfect Squares¶
Longest Increasing Subsequence¶
Number of Longest Increasing Subsequence¶
Longest Increasing Continuous Subsequence¶
序列型 + 状态¶
Paint House¶
Paint House II¶
House Robber¶
House Robber II¶
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock¶
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II¶
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III¶
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV¶
Portfolio Value Optimization¶
There are two questions regarding this problem:
- Can buy fractions of a stock
- Cannot buy fractions of a stock
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <climits>
#include <numeric>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int> curr_price, vector<int> new_price, vector<int> amount, int A) {
int n = curr_price.size();
int f[n + 1][A + 1]; // max profit of the first i stocks with payment j
// init
f[0][0] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= A; ++j) {
f[0][j] = -1;
}
// f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], f[i - 1][j - k * curr_price[i]] + k * new_price[i])
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j <= A; ++j) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
for (int k = 0; k <= amount[i]; ++k) {
if (f[i - 1][j - k * curr_price[i - 1]] != -1 && j >= k * curr_price[i - 1]) {
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - k * curr_price[i - 1]] + k * new_price[i - 1]);
}
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int j = A; j >= 0; --j) {
if (f[n][j] != -1 && f[n][j] > res) {
res = f[n][j];
}
}
return res;
}
};
int main() {
// test1 res = 255
// vector<int> v{15, 40, 25, 30};
// vector<int> w{45, 50, 35, 25};
// vector<int> s{3, 3, 3, 4};
// int m = 140;
// test2 res = 60
vector<int> v{15, 20};
vector<int> w{30, 45};
vector<int> s{3, 3};
int m = 30;
int res = 0;
Solution sol = Solution();
res = sol.maxProfit(v, w, s, m);
cout << res;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <climits>
#include <numeric>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int> curr_price, vector<int> new_price, vector<int> amount, int A) {
int n = curr_price.size();
int f[A + 1]; // max profit of the first i stocks with payment j
// init
f[0] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= A; ++j) {
f[j] = -1;
}
// f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], f[i - 1][j - k * curr_price[i]] + k * new_price[i])
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = A; j >= 0; --j) {
for (int k = 0; k <= amount[i]; ++k) {
if (f[j - k * curr_price[i - 1]] != -1 && j >= k * curr_price[i - 1]) {
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - k * curr_price[i - 1]] + k * new_price[i - 1]);
}
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int j = A; j >= 0; --j) {
if (f[j] != -1 && f[j] > res) {
res = f[j];
}
}
return res;
}
};
int main() {
// test1 res = 255
// vector<int> v{15, 40, 25, 30};
// vector<int> w{45, 50, 35, 25};
// vector<int> s{3, 3, 3, 4};
// int m = 140;
// test2 res = 60
vector<int> v{15, 20};
vector<int> w{30, 45};
vector<int> s{3, 3};
int m = 30;
int res = 0;
Solution sol = Solution();
res = sol.maxProfit(v, w, s, m);
cout << res;
}
划分型¶
Word Break¶
Solution 1 use set dictionary O(n^2), iterate forwards
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
int m = s.length();
unordered_set<string> wordSet(wordDict.begin(), wordDict.end());
bool f[m + 1] = {0};
f[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
if (f[j] && wordSet.count(s.substr(j, i - j)) != 0) {
f[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return f[m];
}
};
Solution 2 use set dictionary O(n^2), iterate backwards
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
int n = s.length();
unordered_set<string> dict(wordDict.begin(), wordDict.end());
int f[n + 1] = {0};
f[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if (f[j] && dict.count(s.substr(j, i - j))) {
f[i] = 1;
break;
}
}
}
return f[n];
}
};
Solution 3 (best solution) use vector, iterate through string
- Do not use word set to check exist or not, use each word as the last step.
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
int n = s.length();
int f[n + 1] = {0};
f[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
for (string word : wordDict) {
if (word.length() <= i && f[i - word.length()]) {
if (s.substr(i - word.length(), word.length()) == word) {
f[i] = 1;
break;
}
}
}
}
return f[n];
}
};
Maximum Vacation Days¶
Solution 1
class Solution {
public:
int maxVacationDays(vector<vector<int>>& flights, vector<vector<int>>& days) {
int n = flights.size();
int k = days[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> f(n, vector<int>(k, -1));
f[0][0] = days[0][0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
if (flights[0][i]) {
f[i][0] = days[i][0];
}
}
for (int d = 1; d < k; ++d) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((flights[j][i] || i == j) && f[j][d - 1] != 1) {
f[i][d] = max(f[i][d], f[j][d - 1] + days[i][d]);
}
}
}
}
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
result = max(result, f[i][k - 1]);
}
return result;
}
};
Solution 2 DFS with Cache
class Solution {
vector<vector<int>> memo;
public:
int maxVacationDays(vector<vector<int>>& flights, vector<vector<int>>& days) {
vector<vector<int>> memo(flights.size(), vector<int>(days[0].size(), INT_MIN));
return dfs(flights, days, 0, 0, memo);
}
int dfs(vector<vector<int>>& flights, vector<vector<int>>& days, int start, int day, vector<vector<int>>& memo) {
if (day == days[0].size()) {
return 0;
}
if (memo[start][day] != INT_MIN) {
return memo[start][day];
}
int maxVal = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < flights.size(); ++i) {
if (flights[start][i] || start == i) {
maxVal = max(maxVal, days[i][day] + dfs(flights, days, i, day + 1, memo));
}
}
memo[start][day] = maxVal;
return maxVal;
}
};
Solution 3 (greedy, wrong)
class Solution {
public:
int maxVacationDays(vector<vector<int>>& flights, vector<vector<int>>& days) {
int n = flights.size();
int k = days[0].size();
int start = 0;
int result = 0;
set<pair<int, int>, std::greater<pair<int, int>>> s;
for (int col = 0; col < k; ++col) {
for (int row = 0; row < n; ++row) {
s.insert({days[row][col], row});
}
int stay = 1;
for (auto p : s) {
if (flights[start][p.second]) {
result += p.first;
cout << p.first << " " << p.second << endl;
start = p.second;
stay = 0;
break;
}
}
if (stay) {
result += days[start][col];
}
s.clear();
}
return result;
}
};
Decode Ways¶
Decode Ways II¶
Solution 1
class Solution {
public:
int numDecodings(string s) {
const int MOD = 1000000007;
int n = s.length();
long long f[n + 1] = {0};
if (n == 0) return 0;
f[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (s[i - 1] == '*') { // not include '0' according to the problem statement
f[i] = (f[i] + f[i - 1] * 9) % MOD; // number of ways only decode one digit
if (i > 1) { // number of ways decode two digits
if (s[i - 2] == '*') {
f[i] = (f[i] + f[i - 2] * 15) % MOD; // 11 - 26
} else if (s[i - 2] == '1') {
f[i] = (f[i] + f[i - 2] * 9) % MOD; // 11 - 19
} else if (s[i - 2] == '2') {
f[i] = (f[i] + f[i - 2] * 6) % MOD; // 21 - 26
}
}
} else { // s[i - 1] != '*', have to consider the case '0'
if (s[i - 1] != '0') { // number of ways only decode one digit
f[i] = (f[i] + f[i - 1]) % MOD;
}
if (i > 1) { // number of ways decode two digits
if (s[i - 2] == '*') {
if (s[i - 1] <= '6') { // '*' can represent 1, 2
f[i] = (f[i] + f[i - 2] * 2) % MOD;
} else { // '*' can only represent 1
f[i] = (f[i] + f[i - 2]) % MOD;
}
} else { // no '*' case
int t = (s[i - 2] - '0') * 10 + s[i - 1] - '0';
if (t >= 10 && t <= 26) {
f[i] = (f[i] + f[i - 2]) % MOD;
}
}
}
}
}
return f[n] % MOD;
}
};
双序列型¶
Longest Common Subsequence¶
Solution 1
- consider the last step, the case is NOT
A[n-1] == B[l-1]andA[n-1] != B[m-1]but, three cases:A[n-1]is included,B[m-1]is included, bothA[n-1]andB[m-1]are included,(A[n-1] == B[m-1]).
Interleaving String¶
Solution 1
class Solution {
public:
bool isInterleave(string s1, string s2, string s3) {
// f[i][j] = OR(f[i][j - 1]|B[j - 1] in C, f[i - 1][j]|A[i - 1] in C);
int m = s1.length();
int n = s2.length();
int l = s3.length();
if (m + n != l)
return false;
int f[m + 1][n + 1] = {0};
f[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n; ++j) {
if (i > 0 && s1[i - 1] == s3[i + j - 1]) {
f[i][j] |= f[i - 1][j];
}
if (j > 0 && s2[j - 1] == s3[i + j - 1]) {
f[i][j] |= f[i][j - 1];
}
}
}
return f[m][n];
}
};
Edit Distance¶
Solution 1
- state:
f[i][j]is min edit distance to make the first i chars of A the same as firstjchars of B, as we consider the last operation (insert, delete, replace). One key idea of this problem is after the operation, the length of the A and B are not necessarilyiandj. The focus here is the "min edit distance", not the length of A or B. For example, if the last step is insert, A's length will becomei + 1, B's length will maintainj. You should also note that the A, B concept is imaginary, B is actually changed from A by editing once. As a result, we knowi + 1 == jafter the insertion operation. Don't iterpret the statef[i][j]as min edit distance of firstichars in A and firstjchars in B and after the editing, A's length isiand B's length isj. You should seperate the two intepretations.
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int m = word1.length();
int n = word2.length();
int f[m + 1][n + 1];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <=n; j++) {
if (i == 0) {
f[i][j] = j;
continue;
}
if (j == 0) {
f[i][j] = i;
continue;
}
// delete insert
f[i][j] = min(f[i - 1][j] + 1, f[i][j - 1] + 1);
// replace
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1);
if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]) {
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return f[m][n];
}
};
Solution 2 Space optimized
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int m = word1.length();
int n = word2.length();
int f[2][n + 1];
int prev = 0, curr = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
prev = curr;
curr = 1 - curr;
for (int j = 0; j <=n; j++) {
if (i == 0) {
f[curr][j] = j;
continue;
}
if (j == 0) {
f[curr][j] = i;
continue;
}
// delete insert
f[curr][j] = min(f[prev][j] + 1, f[curr][j - 1] + 1);
// replace
f[curr][j] = min(f[curr][j], f[prev][j - 1] + 1);
if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]) {
f[curr][j] = min(f[curr][j], f[prev][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return f[curr][n];
}
};
Memoization¶
1049. Last Stone Weight II¶
- Solution 1 Recursion + memoization
- Solution 2 Use two set to simulate
- Solution 3 Transform into knapsack
- Thinking it as adding "+" and "-" in front of each number. The sum of all the numbers with "+" S1, the sum of all number with "-" S2, we want to find the minimum of
|S1 - S2|because we haveS1 + S2 = total. supposeS1 <= S2, we want to minimizeS2 - S1 = total - S1 - S1 = total - 2 * S1; We wil achieve the goal by maximizingS1, so that the stete would be.f[i][j]represent the optimal value of use firstistones to achieve maximumj(S1) value.
- Thinking it as adding "+" and "-" in front of each number. The sum of all the numbers with "+" S1, the sum of all number with "-" S2, we want to find the minimum of
class Solution {
int memo[30][3001];
public:
int lastStoneWeightII(vector<int>& stones) {
return helper(stones, 0, 0);
}
int helper(vector<int>& stones, int i, int sum) {
if (i == stones.size())
return abs(sum);
if (memo[i][sum] != 0)
return memo[i][sum];
memo[i][sum] = min(helper(stones, i + 1, abs(sum - stones[i])),
helper(stones, i + 1, sum + stones[i]));
return memo[i][sum];
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int lastStoneWeightII(vector<int>& stones) {
if (stones.size() == 0)
return 0;
unordered_set<int> set_left({stones[0]});
for (int i = 1; i < stones.size(); ++i) {
unordered_set<int> set_right = set_left;
set_left.clear();
for (int y : set_right) {
set_left.insert(y + stones[i]);
set_left.insert(y - stones[i]);
}
}
int ans = INT_MAX;
for (int z : set_left) {
ans = min(ans, abs(z));
}
return ans;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int lastStoneWeightII(vector<int>& stones) {
int n = stones.size();
int sum = accumulate(begin(stones), end(stones), 0);
vector<vector<int>> f(n + 1, vector<int>(sum / 2 + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j < sum / 2 + 1; ++j) {
if (j < stones[i - 1]) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
} else {
f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], f[i - 1][j - stones[i - 1]] + stones[i - 1]);
}
}
}
return sum - 2 * f[n][sum / 2];
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int lastStoneWeightII(vector<int>& stones) {
int n = stones.size();
int sum = accumulate(begin(stones), end(stones), 0);
vector<int> f(sum / 2 + 1, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = sum / 2; j >= 0; --j) {
if (j >= stones[i - 1]) {
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - stones[i - 1]] + stones[i - 1]);
}
}
}
return sum - 2 * f[sum / 2];
}
};
Sentence Screen Fitting¶
Solution 1
- You can view the sentence as a space seperated English sentence and then use each row to "frame" the sentence. If the end of the frame overlap a space, we continue move to the next frame if available. If the end of the frame overlap a character, we should move the right the frame to the end of the prev word and move on to the next frame.
class Solution {
public:
int wordsTyping(vector<string>& sentence, int rows, int cols) {
int n = sentence.size();
string s;
for (string w : sentence) {
s += string(w + " ");
}
int start = 0, len = s.length(); //s with an extra trailing space.
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
start += cols;
if (s[start % len] == ' ') {
++start;
} else {
while (start > 0 && s[(start - 1) % len] != ' ') {
--start;
}
}
}
return start / len;
}
};
Solution 2
- One insight of this solution is that every word in the sentence is possible to start a new row, but not necessary. For example, a long row can contain multiple of the setences, but the last word cannot fit into this sigle row, it start a new row. In this case only the first word in the sentence and the last word can start a new row. We use this insight in the following way, for each word, we assume it could start a new row, then use the following words in the sentence to fix the row, we record the total number of words that can fit this row in
dp[i],iis the index of the starting word in the sentence. After the calculation, we could countsum(dp[i]),iis starting word's index.
class Solution {
public:
int wordsTyping(vector<string>& sentence, int rows, int cols) {
int n = sentence.size();
int f[n] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int len = 0, count = 0, idx = i;
while (len + sentence[idx % n].length() <= cols) {
len += (sentence[idx % n].length() + 1);
idx++;
count++;
}
f[i] = count;
}
int total = 0;
for (int i = 0, idx = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
total += f[idx];
idx = (f[idx] + idx) % n;
}
return total / n;
}
};
TODO: This solution may be further improved because for some of the count, we never used. Can we calculate the final result by only one loop, or in a nested loop?